Filing taxes often leaves individuals feeling overwhelmed. Moreover, small businesses find it hard to match the timelines and cope with changing rules and regulations. In addition to that, the multitude of forms and specific requirements can lead to further confusion and mistakes. For CPAs and accounting firms, ensuring clients complete their 1040 form accurately is inevitable. Undoubtedly, the errors result in penalties. Moreover, these errors undermine client trust and satisfaction.
The 1040 form stands at the core of individual income tax reporting in the United States. Mastering this form is essential for tax professionals aiming to deliver precise and reliable services. This comprehensive guide delves into every aspect of the 1040 form, equipping CPAs and accounting firms with the knowledge needed to assist their clients effectively.
What is IRS Form 1040?
The 1040 form serves as the cornerstone of federal income tax reporting for U.S. taxpayers. Taxpayers use this essential document to report their earnings from various sources, including wages, salaries, dividends, and other income streams. It calculates an individual’s total tax liability and determines whether they owe additional taxes or are entitled to a refund. The IRS requires every U.S. taxpayer who meets specific filing requirements to complete this form, making it a critical component of the federal tax system.
The government introduced the 1040 form in 1913, after the ratification of the 16th Amendment. This introduction marked a significant shift in U.S. tax policy by establishing a federal income tax system. The form has undergone numerous revisions to align with changes in tax laws, economic conditions, and policy goals.
Staying updated on instructions for form 1040 and the latest requirements for the 1040 individual income tax return ensures that clients receive the most accurate and timely advice on completing their IRS Form 1040.
Diverse Variants of IRS Form 1040

The 1040 form comes in several versions, each tailored to specific taxpayer circumstances. These variants include:
1040-SR
- Tailored for seniors aged 65 and older.
- Features larger print and a simplified layout.
- Includes a standard deduction chart for easy reference.
- Mirrors the content of the standard 1040 individual income tax return.
- Designed to reduce stress and improve accessibility for older taxpayers.
1040-NR
- Intended for non-resident aliens with U.S.-sourced income.
- Used instead of the standard 1040 form to report U.S.-based earnings.
- Includes sections for taxable and non-taxable income under U.S. tax treaties.
- Ensures accurate reporting and compliance with U.S. tax laws.
1040X
- Used for amending previously filed tax returns.
- Corrects errors or adjusts information on the original IRS Form 1040.
- Allows taxpayers to update filing status, income, or claim overlooked deductions/credits.
- Important for rectifying tax records, potentially receiving refunds, or reducing amounts owed.
- Filing promptly ensures compliance with IRS regulations and avoids penalties.
Key Sections of IRS Form 1040

Essential Personal Information
The 1040 form begins with capturing essential personal details. This section requires the taxpayer’s filing status, the number of dependents, and other relevant personal information. Entering accurate data is crucial as it influences tax calculations and eligibility for various credits and deductions. Any errors in this foundational step can lead to discrepancies in the tax return or missed opportunities for valuable tax benefits. Ensuring correctness in this section sets the stage for a smooth and accurate filing process.
Detailed Income Reporting
A critical component of the 1040 form is the reporting of income. Taxpayers must disclose all sources of income, which include wages from employment, dividends and interest from investments, and retirement income such as pensions or Social Security benefits. Comprehensive and precise reporting is vital to avoid discrepancies that could trigger IRS audits or result in penalties for underreporting income. Proper documentation and accurate reporting of all income sources help in maintaining compliance with tax laws and avoiding potential issues with the IRS.
Deductions and Credits Explained
Understanding deductions and credits is essential for optimizing tax benefits. The 1040 form offers two main deduction options. The Standard Deduction provides a fixed amount based on the taxpayer’s filing status, simplifying the filing process but potentially offering less tax benefit than itemizing. On the other hand, Itemized Deductions involve detailed expenses such as mortgage interest, medical expenses, and charitable contributions, which require meticulous record-keeping but can lead to greater tax savings. In addition to deductions, various tax credits like the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and Child Tax Credit can further reduce tax liabilities. Navigating these sections effectively can maximize potential tax savings and ensure accurate and beneficial filings.
Tax and Refund Calculation
The final section of the 1040 form involves calculating the total tax owed or the refund due. This calculation requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure that all reported income, deductions, and credits are accurately accounted for. Precision in this step is essential to avoid financial discrepancies and maintain compliance with IRS guidelines. Accurate calculations help in determining the correct tax outcome and prevent further issues or adjustments with the IRS, ensuring a smooth conclusion to the filing process.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Inaccurate Income Reporting
One common error on the 1040 form is inaccurate income reporting. Omitting a source of income or misreporting amounts can lead to penalties and increased tax liabilities. CPAs must verify all income entries against the instructions for Form 1040 to ensure completeness and accuracy. This prevents costly errors and keeps the 1040 individual income tax return compliant with IRS regulations.
Additionally, ensuring accurate income reporting helps avoid IRS scrutiny. Mistakes can trigger audits and complications. By carefully checking income details against documentation and following the IRS Form 1040 guidelines, tax professionals safeguard their clients from unnecessary issues and maintain accurate returns.
Calculation Errors and Filing Status Missteps
Calculation errors can skew the final tax liability or refund amount on the 1040 form. Even minor mistakes affect the tax return’s accuracy. Double-checking all calculations and totals, as detailed in the instructions for Form 1040, is essential to avoid discrepancies. This practice ensures that the final tax outcome is correct and minimizes the risk of errors.
Selecting the wrong filing status on the 1040 individual income tax return can also impact eligibility for deductions and credits. Incorrect status choices might lead to missed tax benefits. Confirming the correct filing status and reviewing entries according to the IRS Form 1040 instructions ensures clients receive all possible tax advantages and avoid complications with the IRS.
Overlooking Deductions and Credits
Taxpayers often overlook valuable deductions and credits, reducing their potential savings. Missed opportunities, such as education credits or student loan interest deductions, result in higher tax bills. CPAs should review client information thoroughly to ensure all applicable tax benefits are claimed as outlined in the instructions for Form 1040.
A comprehensive review helps uncover missed deductions and credits. This proactive approach maximizes savings and ensures accurate tax filings. By identifying all possible tax incentives on the 1040 form, CPAs enhance client outcomes and improve the efficiency of the tax preparation process.
Essential Tax Planning Strategies
Organized record-keeping is crucial for effective tax planning. Accurate documentation of income, expenses, and deductions simplifies the preparation of the 1040 form. Encouraging clients to maintain detailed records throughout the year supports accurate and efficient filing of the 1040 individual income tax return.
Staying updated on tax law changes is also vital. Frequent updates can impact the 1040 form and tax preparation. Tax professionals should continuously educate themselves on the latest regulations to provide accurate advice and ensure compliance with the IRS Form 1040. This helps maintain high-quality service and accurate tax returns.
Filing Deadlines and Penalties
Key Filing Deadlines
Meeting the filing deadlines for the 1040 form is essential to avoid penalties. The usual deadline is April 15th, but taxpayers can apply for an extension if needed. Keeping track of these dates and planning ahead helps ensure the timely submission of the 1040 individual income tax return.
Penalties for Late Filing
Failing to file the 1040 form on time can lead to significant penalties and interest charges. The IRS imposes a late filing penalty of 5% of unpaid taxes for each month the return is overdue, up to a maximum of 25%. Additionally, interest accrues on any unpaid taxes from the due date until the full amount is paid. Timely filing helps clients avoid these unnecessary financial burdens.
Extension and Payment Solutions
If clients cannot meet the April deadline, they can request an extension, typically extending the filing deadline to October 15th. However, this extension only applies to the filing date, not the payment deadline. Clients must estimate their tax liability and pay any taxes owed by the original deadline to avoid penalties.
How Outsourcing the 1040 Individual Income Tax Return to CapActix Can Benefit CPA Firms
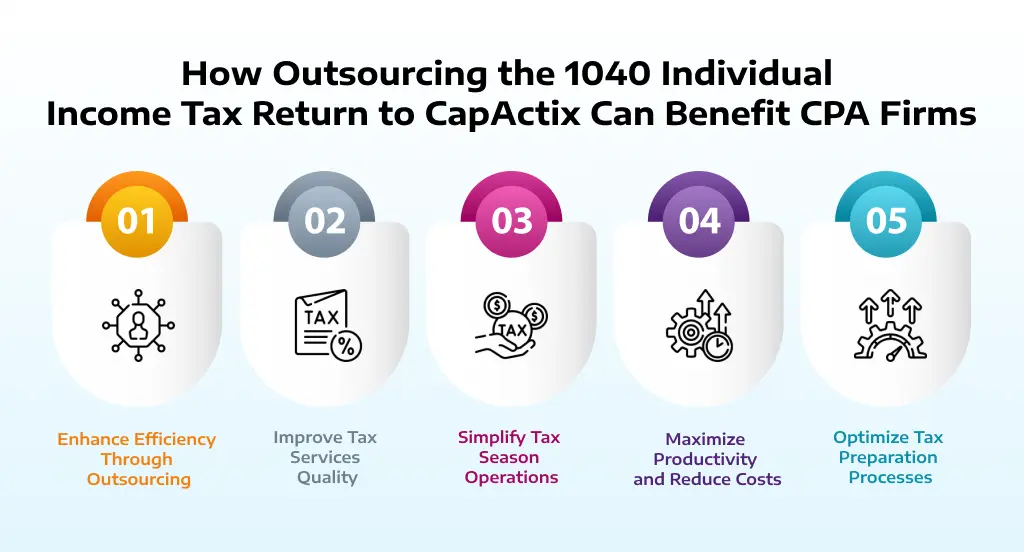
Enhance Efficiency Through Outsourcing
Outsourcing the preparation of 1040 individual income tax returns can greatly boost a CPA firm’s efficiency. By delegating tax preparation tasks, firms can streamline their processes and focus more on strategic client services.
Improve Tax Services Quality
Outsourcing 1040 returns allows CPA firms to elevate the quality of their tax services. This approach ensures that tax returns are handled by specialists, which enhances accuracy and client satisfaction.
Simplify Tax Season Operations
Outsourcing during tax season helps firms manage the increased workload more effectively. By transferring 1040 return preparation to external experts, firms can streamline operations and reduce stress during peak periods.
Maximize Productivity and Reduce Costs
Utilizing outsourcing for 1040 returns can lead to greater productivity and cost savings. Firms benefit from reduced administrative overhead and can reallocate resources to more value-added activities.
Optimize Tax Preparation Processes
Outsourcing the 1040 individual income tax return process allows firms to optimize their tax preparation workflow. It ensures precision in handling returns while minimizing the internal administrative burden.
FAQs
CPAs should stay updated annually. Moreover, when there are changes in tax laws or IRS regulations that affect the 1040 form, CPAs need to upgrade their knowledge.
Yes, the 1040X form is used to amend previously filed 1040 forms to correct errors or make adjustments.
Common deductions include mortgage interest, student loan interest, medical expenses, and charitable contributions, among others.
Conclusion
Effective tax planning pivots on organized bookkeeping and staying informed about tax law changes. Implementing these strategies, tax professionals can enhance their service offerings and build stronger client relationships. Moreover, outsourcing the preparation of 1040 individual income tax returns to specialists streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve accuracy. This allows CPA firms to focus on delivering exceptional financial guidance.
We are one of the leading outsourcing companies that have expertise in tax preparation. We understand the knitty gritty of 1040 form. To book a free consultation, please connect with us.
















